- January 13, 2022
- A2K WordPress
- 0
- CAD vs BIM: What’s the Difference?
- January 31, 2022

Computer-aided design (CAD) and Building Information Modeling (BIM) are concepts integral to the AEC industry, but what are they? And what are the key differences?
It’s essential to know the differences between traditional computer-aided design and building information modeling, especially for those in the AEC industry. As a result, understanding the differences between the two can help you make the best decision on your upcoming projects.
CAD is the practice of using computer systems to help with the design. In designing buildings, CAD is the use of a drafting tool to create lines and arcs that represent a the design of said structure.
In our BIM 101 for AEC Professionals Webinar, we address what BIM is and is not. But we’ve highlighted a few of the key differences here.
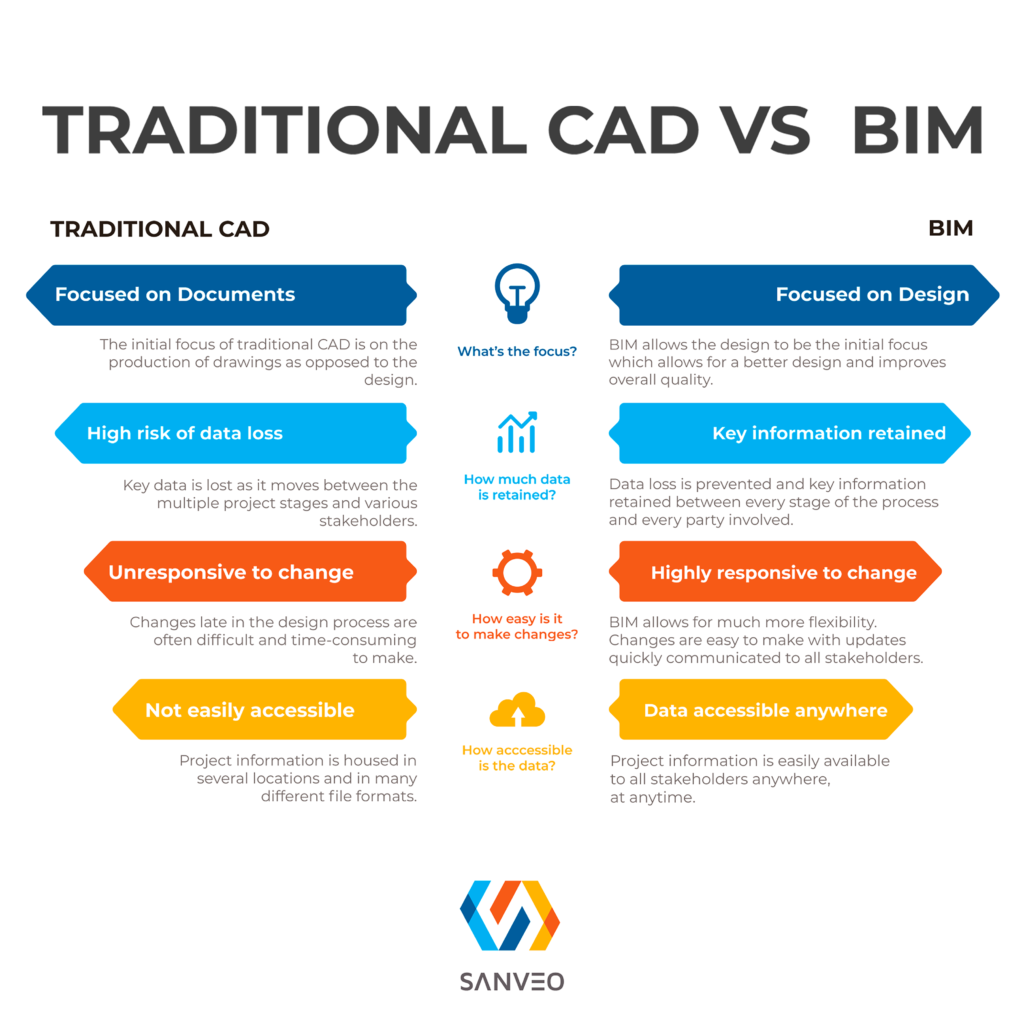
BIM’S FOCUS ON DESIGN ALLOWS FOR BETTER DESIGN AND QUALITY
Building Information Modeling allows the design to be the initial focus, resulting in a higher quality design. On the contrary, the initial focus of CAD is on the production of drawings only and not on the design of the structure.
RETAIN KEY INFORMATION BETWEEN EVERY STAGE WITH BIM
With CAD information is typically lost as it moves between the multiple project stages and stakeholders. On the other hand, building information modeling prevents data loss and ensures the retention of essential information for all parties involved throughout the process.
BIM IS HIGHLY RESPONSIVE TO CHANGES
BIM allows for much more flexibility. Therefore, necessary changes can easily be made, with updates quickly communicated to all stakeholders. In contrast, any adjustments made late in the CAD design process are often challenging and time-consuming to make.
DATA IS ACCESSIBLE ANYWHERE, AT ANY TIME
With CAD, project information lives in several locations and is in many different file formats. In contrast, the adoption of building information modeling simplifies this process, with project information easily accessible to all stakeholders wherever they are3